Language models and ChatGPT are both AI-powered language tools, but they differ in their training data, architecture, capabilities, and use cases. Here's a quick overview:
Language Models
- Trained on vast datasets of text from various sources
- Designed for tasks like text generation, language translation, and sentiment analysis
- Use transformer-based architecture
ChatGPT
- Trained on conversational data, optimized for dialogue
- Designed for chatbot applications, customer support, and content generation
- Understands context, generates creative content
- Variant of GPT-3 with specialized architecture for chatbots
Quick Comparison
| Feature | Language Models | ChatGPT |
|---|---|---|
| Training Data | Large text datasets | Conversational data |
| Architecture | Transformer-based | Variant of GPT-3 |
| Capabilities | Text generation, NLP tasks | Conversational interactions, creative content |
| Use Cases | Language translation, text summarization | Chatbots, customer support, content generation |
| Strengths | Process large data, generate text | Understand context, creative responses |
| Weaknesses | Can be biased, computationally expensive | Prone to inaccuracies, lacks emotional intelligence |
The key difference lies in ChatGPT's specialized training and architecture for conversational interactions, while language models are more general-purpose tools for various NLP tasks. Choosing the right tool depends on the specific use case and requirements.
What Are Language Models?
Language models are a crucial part of natural language processing (NLP) and have revolutionized the way machines understand and generate human-like language. In simple terms, a language model is a statistical tool that predicts the probability of a sequence of words in a language.
How Language Models Work
Language models work by analyzing patterns and structures in large amounts of text data. This analysis enables them to:
- Generate original text
- Predict the next word in a sentence
- Perform various language-based tasks such as text summarization, machine translation, and speech recognition
Types of Language Models
There are several types of language models, including:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| N-gram | Predicts the probability of a word based on the previous n-1 words |
| Unigram | Predicts the probability of a word based on its individual characteristics |
| Bidirectional | Analyzes the context of a word from both the left and right sides |
| Neural | Uses artificial neural networks to analyze complex patterns in text |
Applications of Language Models
Language models have many applications, including:
- Chatbots and virtual assistants
- Language translation
- Text generation
- Speech recognition
In the context of ChatGPT, language models are specifically designed for conversational interactions, enabling machines to understand and respond to human input in a more natural and intuitive way.
By understanding the basics of language models, we can better appreciate their potential to transform various industries and aspects of our lives. In the next section, we will delve deeper into the unique features and capabilities of ChatGPT, a specific type of language model designed for conversational interactions.
ChatGPT: A Unique Language Tool
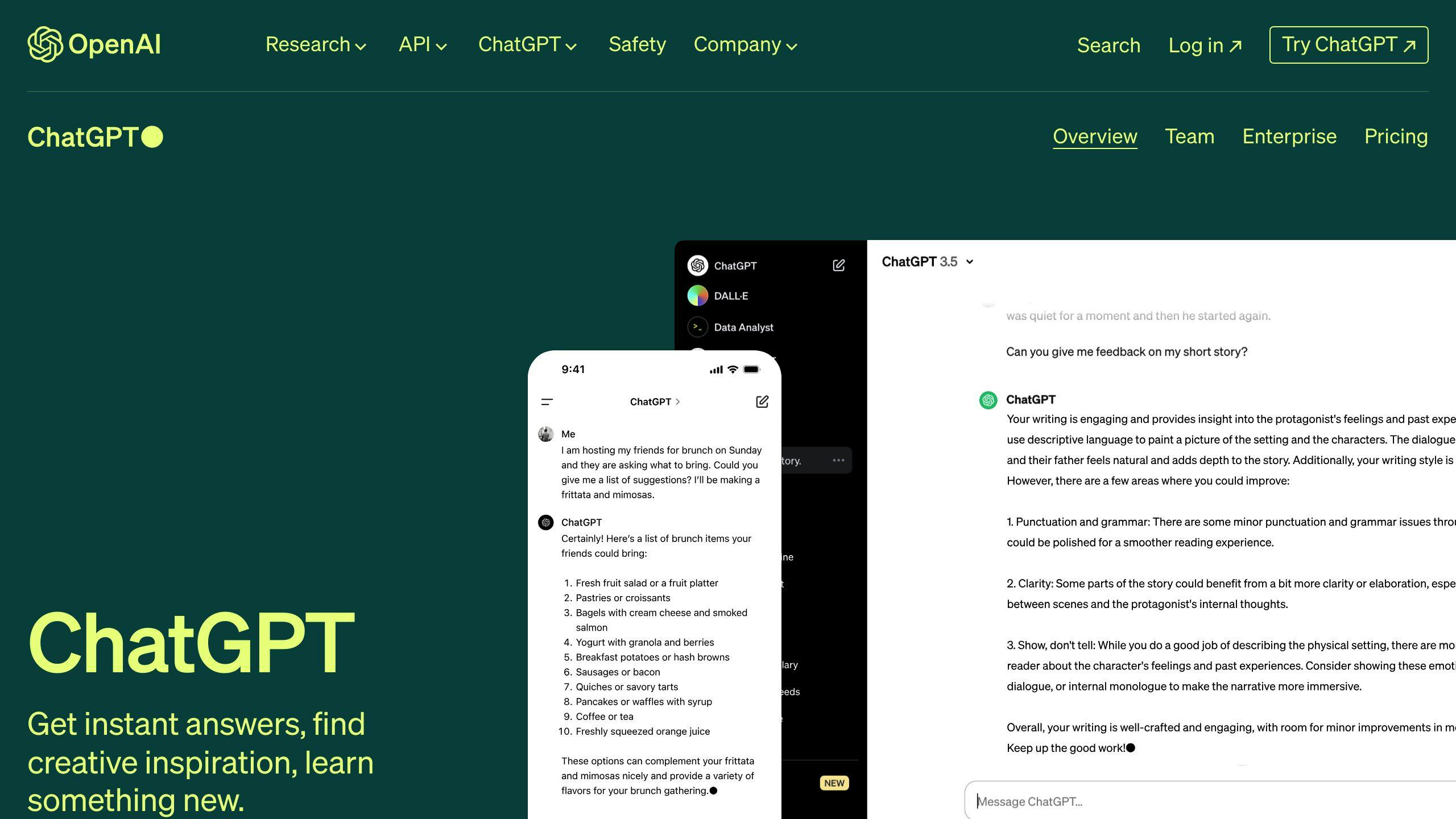
ChatGPT is a specific type of language model designed for conversational interactions. It's trained on conversational data to improve its ability to generate human-like responses in a dialogue context.
Understanding Context and Intentions
ChatGPT differs from other language models in its ability to understand the context in which words are being spoken, as well as the intentions and emotions of the speakers. This is achieved through its training on data from real-world conversations.
Generating Conversational Responses
ChatGPT stands out in its ability to generate responses that are more appropriate for a conversation. Many language models can generate text that is coherent and grammatically correct, but may not always generate responses that are suitable for the context or feel natural in a conversation.
Training Architecture
ChatGPT's training architecture involves a two-step process:
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Unsupervised | Exposed to a vast array of Internet text, enabling it to learn language patterns, semantic structures, and even trivia. |
| Fine-tuning | Trained on a narrower dataset with human supervision, tailoring its abilities to accomplish specific tasks like responding to prompts or carrying out a conversation. |
This two-step training strategy distinguishes ChatGPT, ensuring that it's not just producing text, but meaningful, contextually coherent dialogue.
Overall, ChatGPT's unique training process and conversational focus make it a powerful tool for natural language processing tasks, particularly those that involve human-like conversation.
Language Models vs. ChatGPT: Key Differences
Language models and ChatGPT are both AI-powered language tools, but they have distinct differences in their training data, architecture, capabilities, and use cases. Understanding these differences is crucial in choosing the right tool for specific tasks and applications.
Training Data Comparison
| Tool | Training Data |
|---|---|
| Language Models | Vast amounts of text data (books, articles, research papers, websites) |
| ChatGPT | Conversational data (dialogue and interactions) |
Language models are trained on broad datasets, enabling them to learn general language patterns and semantic structures. ChatGPT, on the other hand, is trained on targeted conversational data, allowing it to understand context, intentions, and emotions.
Architecture Differences
Language models typically employ a transformer-based architecture, designed for sequential data processing. ChatGPT uses a modified transformer architecture that incorporates additional components, such as attention mechanisms and memory modules, to handle conversational inputs and generate contextually relevant responses.
Capabilities Overview
| Tool | Capabilities |
|---|---|
| Language Models | Text generation, language translation, sentiment analysis, question answering |
| ChatGPT | Conversational interactions, understanding context, responding to questions and prompts |
Language models are capable of performing a wide range of NLP tasks, while ChatGPT is specifically designed for conversational interactions.
Use Case Examples
| Tool | Use Cases |
|---|---|
| Language Models | Language translation, text summarization, chatbots, research |
| ChatGPT | Customer support, virtual assistants, conversational interfaces |
By understanding the key differences between language models and ChatGPT, developers and businesses can choose the right tool for their specific needs and applications, leading to more effective and efficient language processing solutions.
sbb-itb-b2c5cf4
Pros and Cons Analysis
An unbiased examination of the advantages and limitations of language models and ChatGPT, helping readers understand the practical implications of using these technologies.
Language Model Strengths and Weaknesses
Strengths
- Process and analyze large amounts of data
- Generate human-like text
- Perform various NLP tasks such as language translation and sentiment analysis
- Can be fine-tuned for specific tasks
Weaknesses
- Can be biased towards the data they were trained on, leading to inaccurate or unfair results
- Computationally expensive and require significant resources
- May not always understand the context or nuances of human language
ChatGPT Pros and Cons
Pros
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Understands context | Responds accordingly to the conversation |
| Generates creative content | Can produce engaging and creative text |
| Revolutionizes customer service | Can be used to create conversational interfaces |
Cons
| Drawback | Description |
|---|---|
| Prone to inaccuracies | May generate misleading or false information |
| Lacks emotional intelligence | Can lead to insensitive or inappropriate responses |
| Vulnerable to bias | Can perpetuate biases present in the training data |
By understanding the pros and cons of language models and ChatGPT, developers and businesses can make informed decisions about how to use these technologies effectively and responsibly.
Feature Comparison Table
The following table compares the key features of language models and ChatGPT, highlighting their differences in training data, architecture, capabilities, and use cases.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Language Models | ChatGPT |
|---|---|---|
| Training Data | Large datasets of text from various sources | Conversational text data, optimized for dialogue |
| Architecture | Transformer-based architecture | Variant of GPT-3, fine-tuned for chatbot applications |
| Capabilities | Generate human-like text, perform various NLP tasks | Understand context, generate creative content, revolutionize customer service |
| Use Cases | Language translation, text summarization, question answering | Conversational interfaces, customer support, content generation |
| Strengths | Process large amounts of data, generate human-like text | Understands context, generates creative content |
| Weaknesses | Can be biased, computationally expensive | Prone to inaccuracies, lacks emotional intelligence |
| Training Time | Longer training times, require significant resources | Faster training times, optimized for real-time chatbot systems |
| Use in Chatbots | Can be used in chatbots, but not optimized for dialogue | Optimized for chatbot applications, understands context and generates creative content |
This comparison table provides a concise overview of the key differences between language models and ChatGPT, helping readers understand their distinct features and capabilities.
Key Takeaways
In conclusion, understanding the differences between language models and ChatGPT is crucial for individuals and businesses looking to integrate AI into their operations.
Language Models vs. ChatGPT: A Quick Recap
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| Language Models | Large-scale AI systems trained on vast amounts of text data, enabling them to generate human-like text and perform various NLP tasks. |
| ChatGPT | A variant of the GPT-3 language model specifically designed for chatbot applications, optimized for conversational interactions and contextual understanding. |
Choosing the Right AI Tool
By recognizing the strengths and weaknesses of each, businesses can harness the power of AI to:
- Revolutionize customer service
- Generate creative content
- Improve overall operational efficiency
Remember, selecting the right AI tool for specific use cases is vital for achieving success in AI integration.

